Websites Built
For Local Business
I build high-performance websites for tradesmen, salons, and local shops. Leveraging AI tools to deliver secure, cutting-edge sites faster than traditional agencies.
Free Consultation · No Commitments
Helping Local Businesses Dominate Their Market
Modern Tech for
Local Legends
Your business deserves a website that works as hard as you do. I use advanced AI workflows to build secure, fast, and professional sites in a fraction of the time.
Rapid Delivery
Get your plumbing, HVAC, or salon business online fast. My AI-assisted workflow cuts development time from months to weeks.
Secure & Reliable
Security isn't optional. I build sites with improved security standards to protect your business and your customers' data.
Built for Trades
Whether you run a dojo, a grooming service, or an electrical company, I build sites that convert local traffic into paying customers.
3 Steps to a
Better Presence
Strategy Call
We discuss your business goals, target customers, and what makes your brand unique in the local market.
AI-Infused Build
I leverage advanced AI to scaffold your site instantly, spending my focus on custom design and security hardening.
Launch & Dominate
Your site goes live, optimized for performance and local SEO, ready to turn visitors into lifelong customers.
Real Results for
Real Businesses
I don't just build websites; I build digital storefronts that bring customers through your door.
Path Posters
A custom application allowing users to generate and purchase Strava route posters.
- Protomaps
- NextJS
- TypeScript
- DaisyUI
- Lemon Squeezy

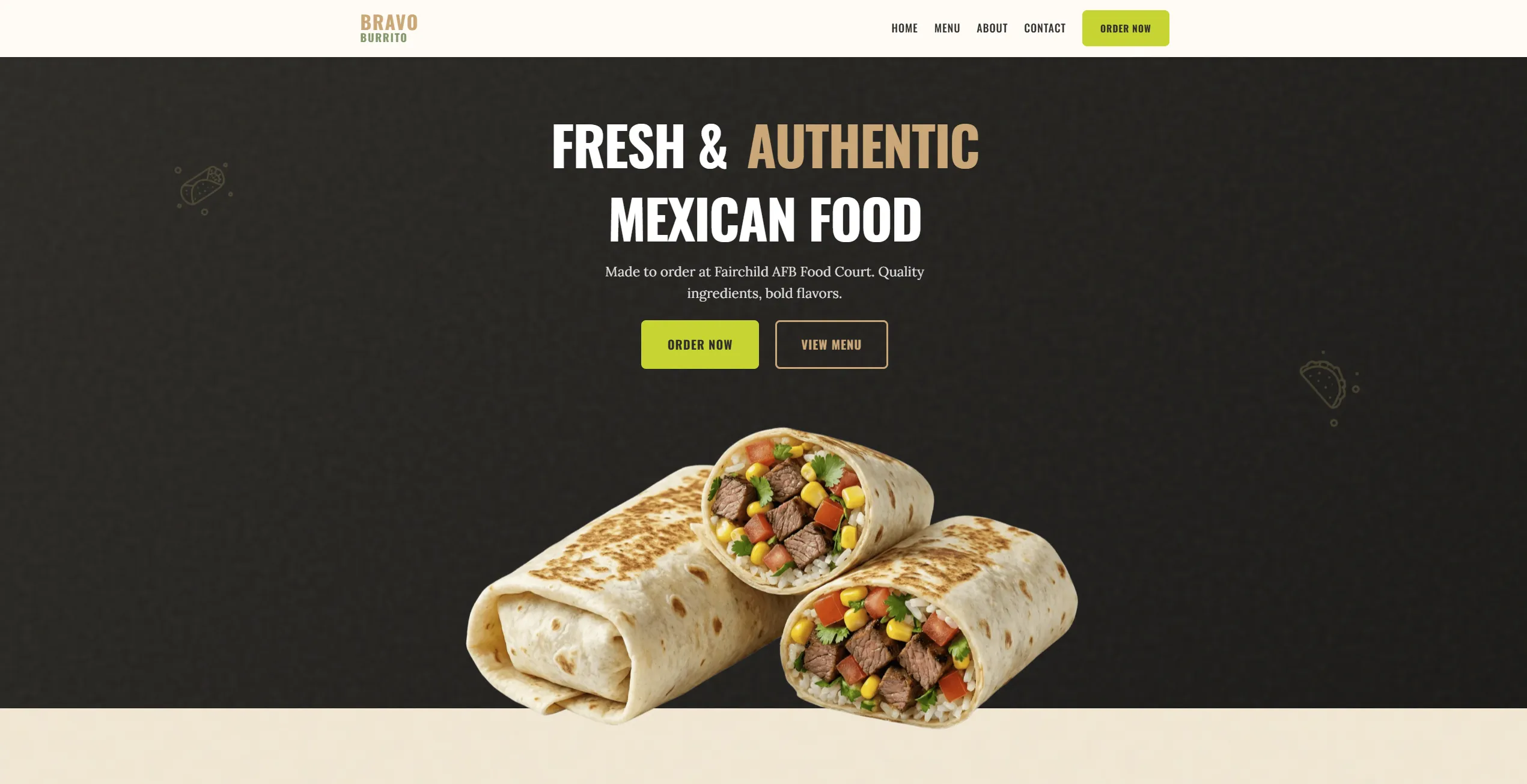
Bravo Burrito
A vibrant, themed website for a local restaurant, capturing the brand's unique Mexican-inspired aesthetic.
View Website
Hartland Coffee
A warm, inviting website for a specialty coffee shop in Spokane, WA, featuring their menu and location.
View Website
Trusted by
Local Legends
"Alexander built my salon website in less than two weeks. It looks high-end and our online booking has doubled ever since."
"As a plumber, I didn't want anything fancy. I just wanted my phone to ring. Alexander delivered a fast, secure site that does exactly that."
Frequently Asked Questions
Let's Build Something
Amazing
Ready to accelerate your roadmap? Tell me about your project.